AJAX Introduction
AJAX is about updating parts of a web page, without reloading the whole page.
What is AJAX?
AJAX = Asynchronous JavaScript and XML.
AJAX is a technique for creating fast and dynamic web pages.
AJAX allows web pages to be updated asynchronously by exchanging small amounts of data with the server behind the scenes. This means that it is possible to update parts of a web page, without reloading the whole page.
Classic web pages, (which do not use AJAX) must reload the entire page if the content should change.
Examples of applications using AJAX: Google Maps, Gmail, Youtube, and Facebook tabs.
How AJAX Works
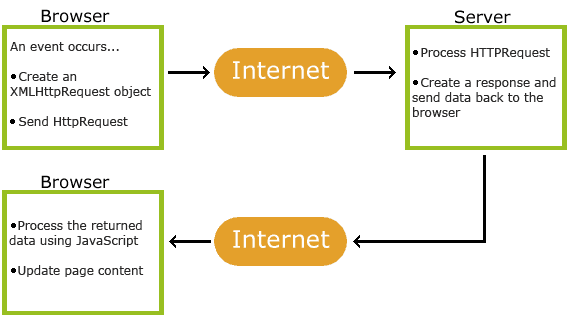
AJAX is Based on Internet Standards
AJAX is based on internet standards, and uses a combination of:
- XMLHttpRequest object (to exchange data asynchronously with a server)
- JavaScript/DOM (to display/interact with the information)
- CSS (to style the data)
- XML (often used as the format for transferring data)
AJAX applications are browser- and platform-independent!
Google Suggest
AJAX was made popular in 2005 by Google, with Google Suggest.
Google Suggest is using AJAX to create a very dynamic web interface: When you start typing in Google's search box, a JavaScript sends the letters off to a server and the server returns a list of suggestions.
Start Using AJAX Today
In our ASP tutorial, we will demonstrate how AJAX can update parts of a web page, without reloading the whole page. The server script will be written in ASP.
If you want to learn more about AJAX, visit our AJAX tutorial.

