What is CSS?
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
CSS describes how HTML elements are to be displayed
CSS Example
<style>
body
{background-color:lightblue; text-align:center;}
h1
{color:blue; font-size:40px;}
p
{font-family:verdana;
font-size:20px;}
</style>
Try it Yourself »
Click on the "Try it Yourself" button to see how it works.
CSS Syntax
A CSS rule consists of a selector and a declaration block:
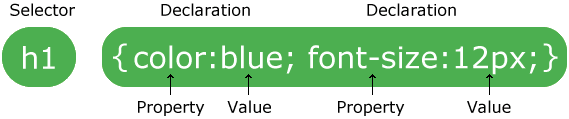
The selector points to the HTML element to style (h1).
The declaration block (in curly braces) contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons.
Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon.
In the following example all <p> elements will be center-aligned, red and have a font size of 32 pixels:
Example
<style>
p
{font-size:32px; color:red;
text-align:center;}
</style>
Same example can also be written like this:
<style>
p
{
font-size: 32px;
color: red;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
Try it Yourself »
External Style Sheet
A CSS style sheet can be stored in an external file:
mystyle.css
body {background-color: orange; font-family:verdana}
h1 {color: white;}
p {font-size: 20px;}
External style sheets are linked to HTML pages with <link> tags:
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="mystyle.css">
<body>
<h1>My First CSS Example</h1>
<p>This is
a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Inline Style
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="mystyle.css">
<body>
<h1>My First CSS Example</h1>
<p>This is
a paragraph.</p>
<p style="font-size:25px">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p style="font-size:30px">This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Cascading Order
If different styles are specified for HTML elements, the styles will cascade into new styles with the following priority:
- Priority 1: Inline styles
- Priority 2: External and internal style sheets
- Priority 3: Browser default
- If different styles are defined on the same priority level, the last one has the highest priority.
Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="mystyle.css">
<style>
body {background-color:
lightblue;}
</style>
<body style="background-color: olivedrab">
<h1>Multiple
Styles Cascades into One</h1>
<p>Try experimenting by removing styles to see how the cascading stylesheets
work.</p>
<p>Try removing the inline first, then the internal, then the
external.</p>
</body>
</html>
CSS Demo - One HTML Page - Multiple Styles!
Here we will show one HTML page displayed with 4 different stylesheets.
Click on the Stylesheet buttons (1-4) too see the page displayed with different styles.
Full CSS Tutorial
This has been a short description of CSS.
For a full CSS tutorial go to W3Schools CSS Tutorial.
For a full CSS reference go to W3Schools CSS Reference.


