Java Multi-Dimensional Arrays
Multidimensional Arrays
A multidimensional array is an array that contains other arrays.
You can use it to store data in a table with rows and columns.
To create a two-dimensional array, write each row inside its own curly braces:
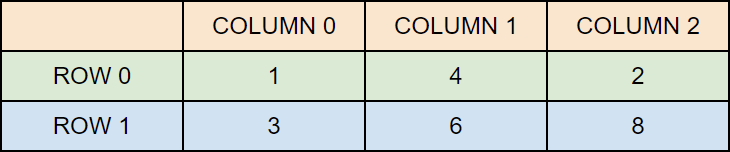
int[][] myNumbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8} };
Here, myNumbers has two arrays (two rows):
- First row:
{1, 4, 2} - Second row:
{3, 6, 8}
Think of it like this:
Access Elements
To access an element of a two-dimensional array, you need two indexes: the first for the row, and the second for the column.
Remember: Array indexes start at 0. That means row 0 is the first row, and column 0 is the first column. (So row index 1 is the second row, and column index 2 is the third column.)
This statement accesses the element in the second row (index 1) and third column (index 2) of the myNumbers array:
Example
int[][] myNumbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8} };
System.out.println(myNumbers[1][2]); // Outputs 8
This example prints the value at row 0, column 1:
Example
int[][] myNumbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8} };
System.out.println(myNumbers[0][1]); // Outputs 4
Change Element Values
You can overwrite an existing element using the same two-index notation (row, then column):
Example
int[][] myNumbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8} };
myNumbers[1][2] = 9;
System.out.println(myNumbers[1][2]); // Outputs 9 instead of 8
Rows and Columns (Lengths)
You can use length to get the number of rows, and
myNumbers[row].length for the number of columns in a given row:
Example: Sizes
int[][] myNumbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8, 5, 2} };
System.out.println("Rows: " + myNumbers.length); // 2
System.out.println("Cols in row 0: " + myNumbers[0].length); // 3
System.out.println("Cols in row 1: " + myNumbers[1].length); // 5Note: Notice how rows can have different lengths - In this example, the second row has more elements than the first, and that's perfectly valid in Java.
Loop Through a Multidimensional Array
Use a for loop inside another for loop to visit every element (row by row):
Example
int[][] myNumbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8, 5, 2} };
for (int row = 0; row < myNumbers.length; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < myNumbers[row].length; col++) {
System.out.println("myNumbers[" + row + "][" + col + "] = " + myNumbers[row][col]);
}
}Or use a for-each loop in both levels, which many find easier to read:
Example
int[][] myNumbers = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8, 5, 2} };
for (int[] row : myNumbers) {
for (int num : row) {
System.out.println(num);
}
}
