AWS Cloud Auto Scaling
EC2 Auto Scaling
When servers receive more requests than they can handle, it can cause timeouts and outages. EC2 Auto Scaling automatically adds or removes instances to match demand.
EC2 Scaling Video (Part 2)
W3schools.com collaborates with Amazon Web Services to deliver digital training content to our learners.
Two Approaches to EC2 Auto Scaling
- Dynamic scaling: responds to changing demand in real-time
- Predictive scaling: schedules instances based on predicted demand
You can combine both approaches for faster scaling.
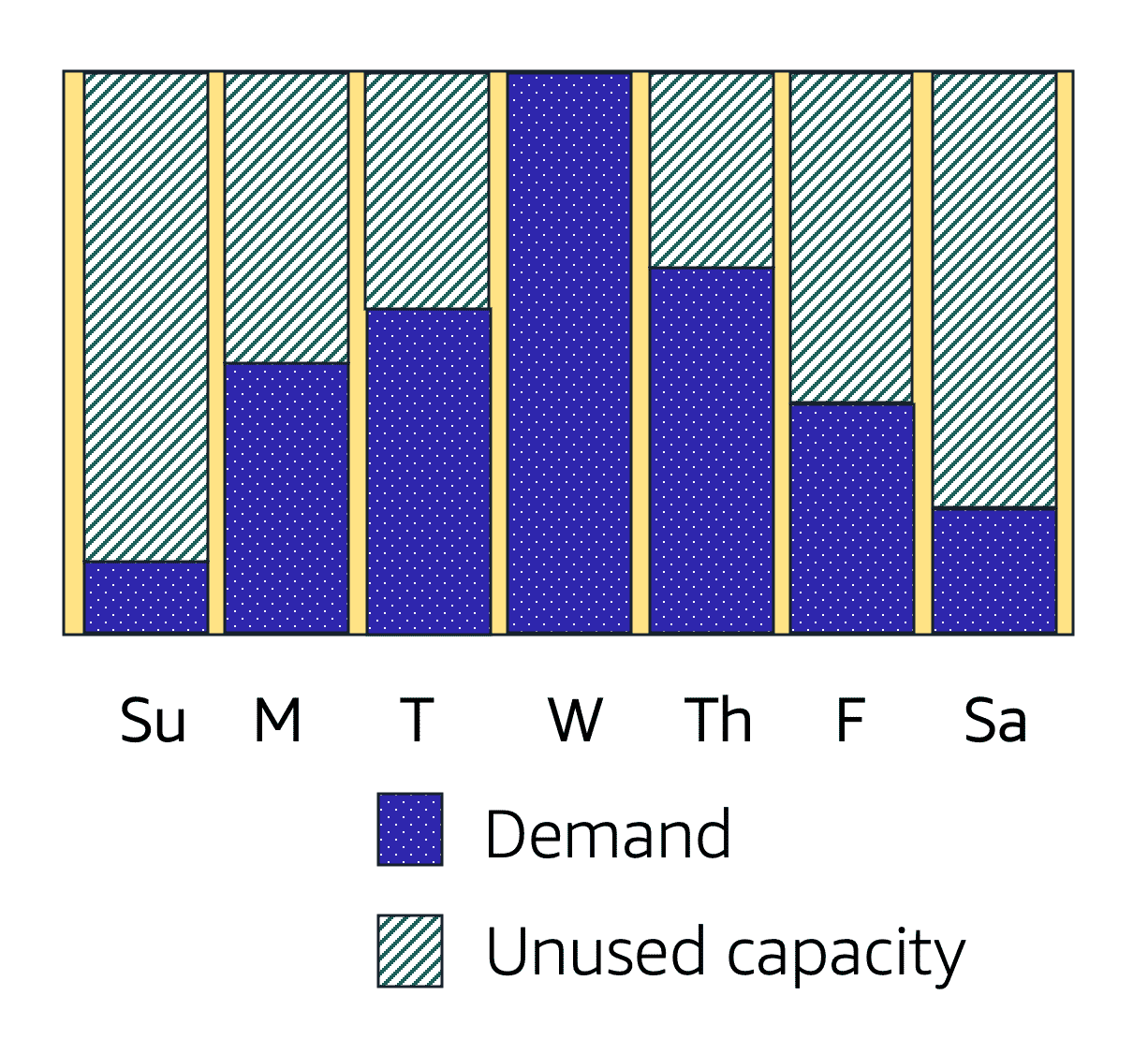
Image created by Amazon Web Services
Auto Scaling Groups
An Auto Scaling group is a collection of EC2 instances. You define capacity limits:
- Minimum: Always keep at least this many instances running
- Desired: Ideal number of instances for normal traffic
- Maximum: Never exceed this many instances (controls costs)
Example: Set min=2, desired=2, max=10. Normally 2 instances run. During traffic spikes, Auto Scaling adds up to 10, then scales back down when traffic drops.

