C Write To Files
Write To a File
Let's use the w mode from the previous
chapter again, and write something to the file we just created.
The w mode means that the file is opened for
writing. To insert content to it, you can use the fprintf()
function and add the pointer variable (fptr in our example) and some text:
Example
FILE *fptr;
// Open a file in writing mode
fptr = fopen("filename.txt", "w");
// Write some text to the file
fprintf(fptr, "Some text");
// Close the file
fclose(fptr);
As a result, when we open the file on our computer, it looks like this:

Note: If you write to a file that already exists, the old content is deleted, and the new content is inserted. This is important to know, as you might accidentally erase existing content.
For example:
Example
fprintf(fptr, "Hello
World!");
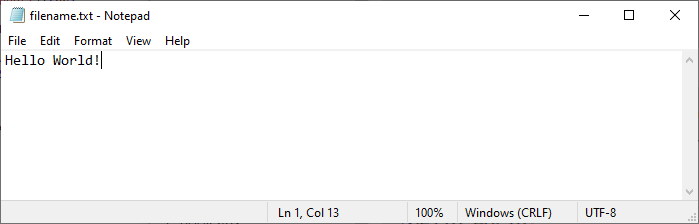
As a result, when we open the file on our computer, it says "Hello World!" instead of "Some text":
Append Content To a File
If you want to add content to a file without deleting the old content, you can use the
a mode.
The a mode appends content at the end of the file:
Example
FILE *fptr;
// Open a file in append mode
fptr = fopen("filename.txt", "a");
// Append some text to the file
fprintf(fptr, "\nHi everybody!");
// Close the file
fclose(fptr);
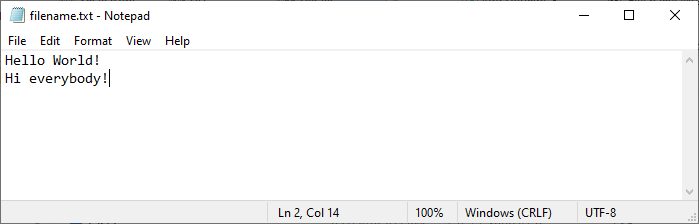
As a result, when we open the file on our computer, it looks like this:
Note: Just like with the w mode; if the file does not exist, the a
mode will create a new file with the "appended" content.

