Excel IFS Function
IFS Function
The IFS function is a premade function in Excel, which returns values based on one or more true or false conditions.
It is typed =IFS and has two or more parts:
=IFS(logical_test1, value_if_true1, [logical_test2, value_if_true2], [logical_test3; ...)
The conditions are referred to as logical_test1, logical_test2, ..., which can check things like:
- If a number is greater than another number
> - If a number is smaller than another number
< - If a number or text is equal to something
=
Each condition is connected with a return value.
Note: More than one condition can be true so the function will return the value for the first true condition.
Note: The different parts of the function are separated by a symbol, like comma , or semicolon ;
The symbol depends on your Language Settings.
Example IFS function
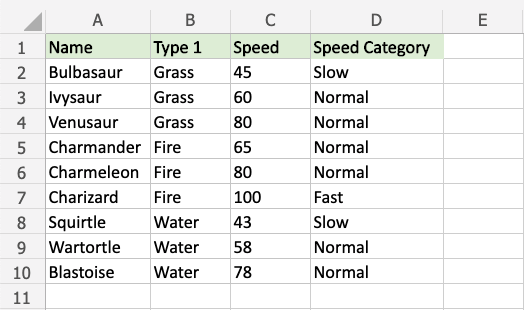
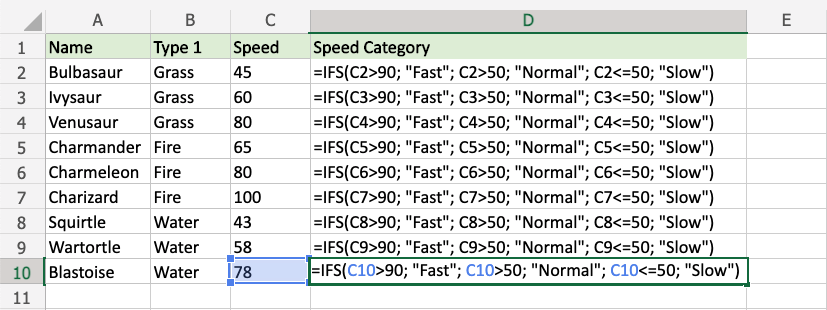
Make categories for how fast the Pokemon are:
The conditions and return values are:
- Speed more than 90: "Fast"
- Speed more than 50: "Normal"
- Speed less than or equal to 50: "Slow"
Example IFS function, step by step:
- Select the cell
D2 - Type
=IFS - Double click the IFS command
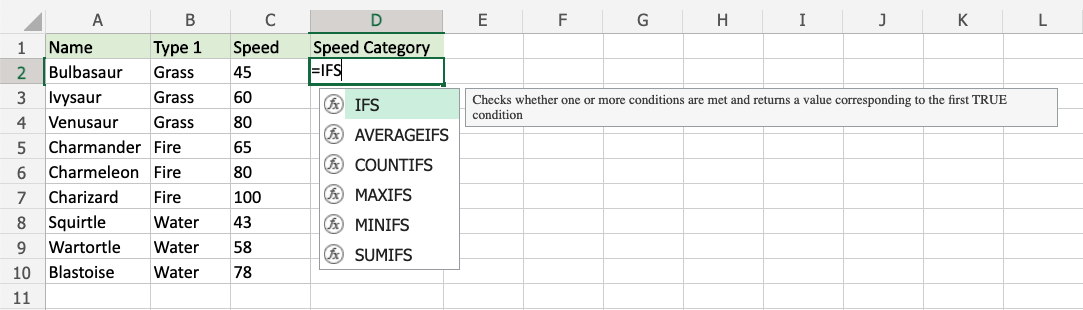
- Specify the first condition
C2>90 - Type
, - Specify the value
"Fast"for when the first condition is TRUE - Type
, - Specify the second condition
C2>50 - Type
, - Specify the value
"Normal"for when the second condition is TRUE - Type
, - Specify the third condition
C2<=50 - Type
, - Specify the value
"Slow"for when the third condition is TRUE - Hit enter
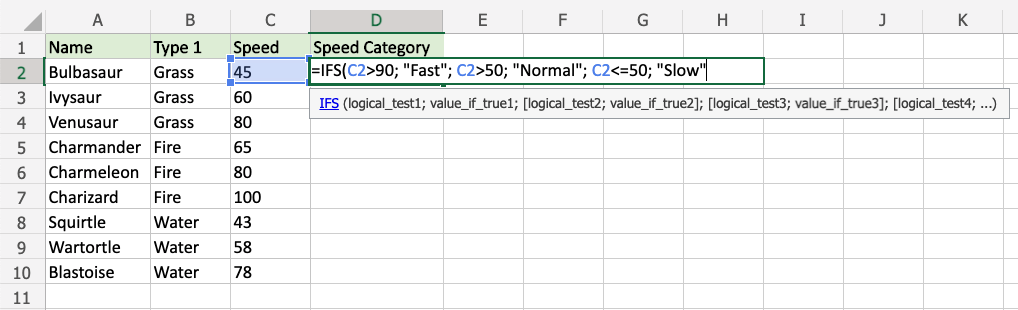
Since the value in cell C2 is "45", the first and second conditions are false, and third condition is true (less than or equal to 50), the function will return "Slow".
Note: Text values needs to be in quotes: " "
The function can be repeated with the filling function for each row to perform the same check for each Pokemon:
Note: The third condition <=50 includes = so that 50 is included in "less than or equal to 50"
Now, each Pokemon has a speed category: