Excel LEFT Function
LEFT Function
The LEFT function is used to retrieve a chosen amount of characters, counting from the left side of an Excel cell. The chosen number has to be greater than 0 and is set to 1 by default.
It is typed =LEFT
If you want to use the function on a single cell, write:
=LEFT(cell)
If you want to use the function on a range of cells, write:
=LEFT(start cell:end cell)
How to Use LEFT Function
To retrieve values from the left side of an Excel cell, use LEFT.
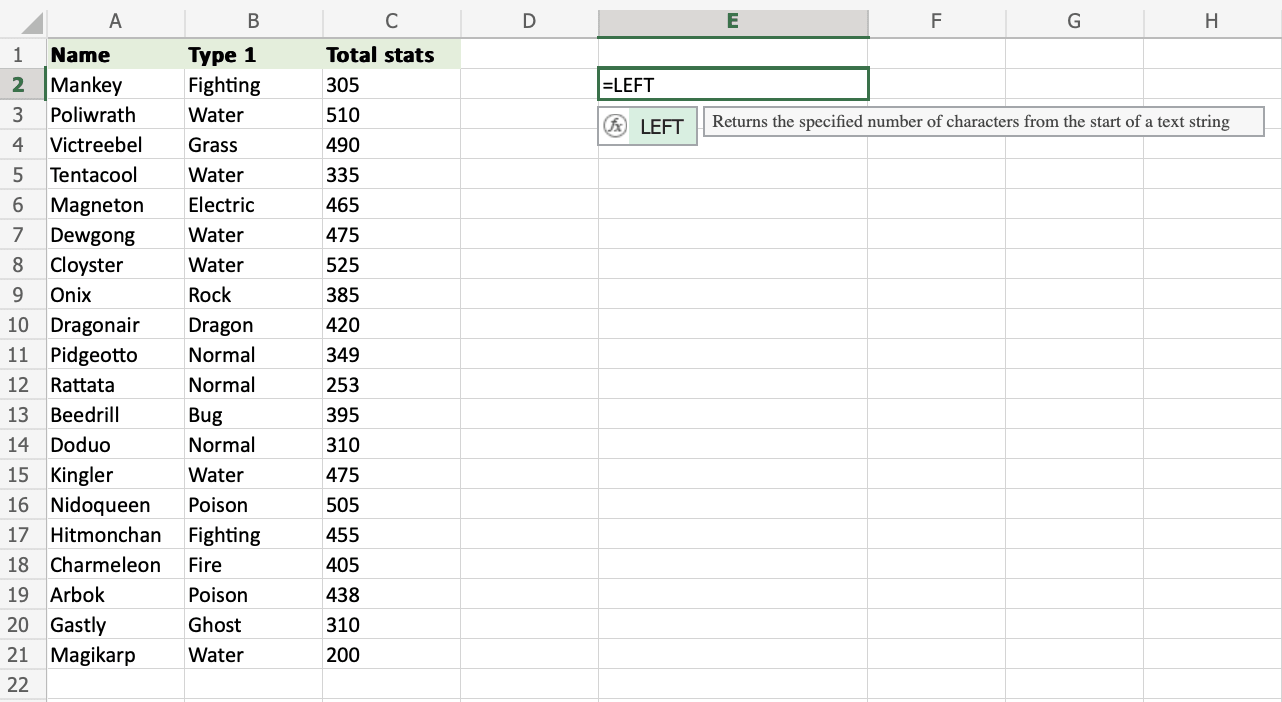
Step 1) Start the LEFT function
- Select a cell
E2 - Type
=LEFT - Double click the LEFT command
Follow along the tutorial by trying it yourself!
Copy the values in the example above and try it on your own!
Step 2) Enter values to the LEFT function
- Select a cell (
A2) - Hit enter
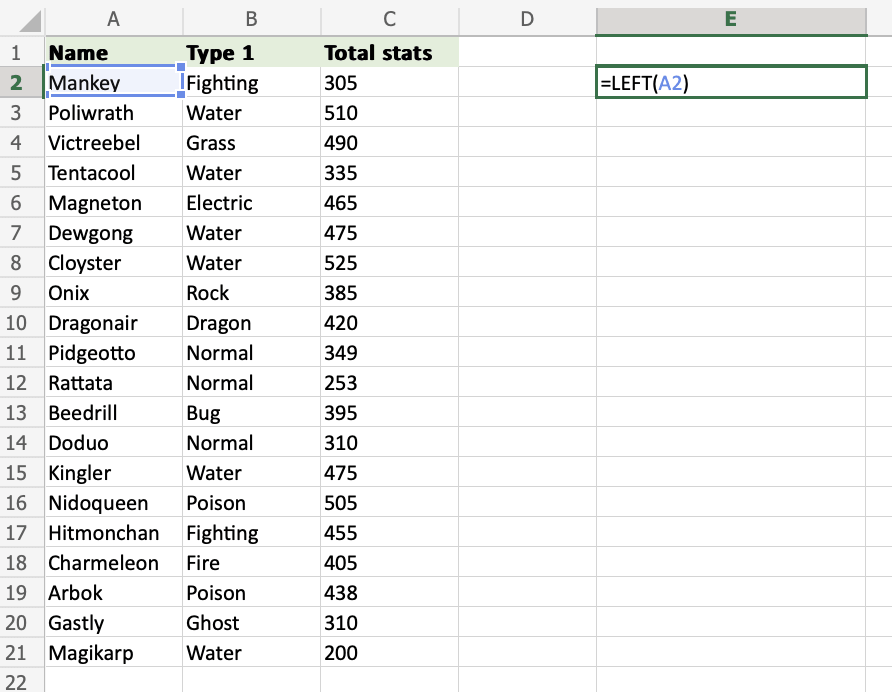
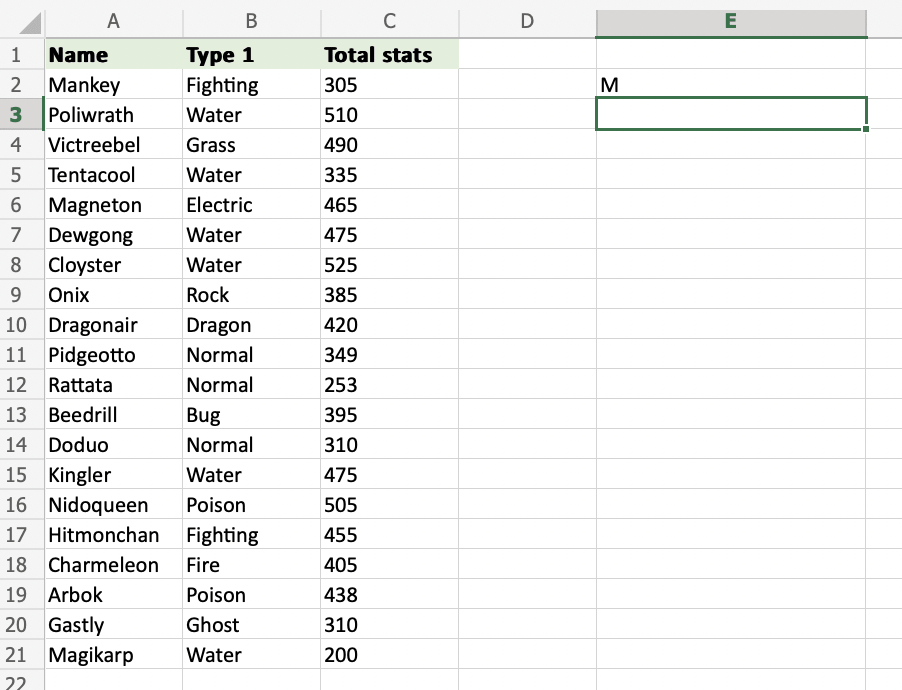
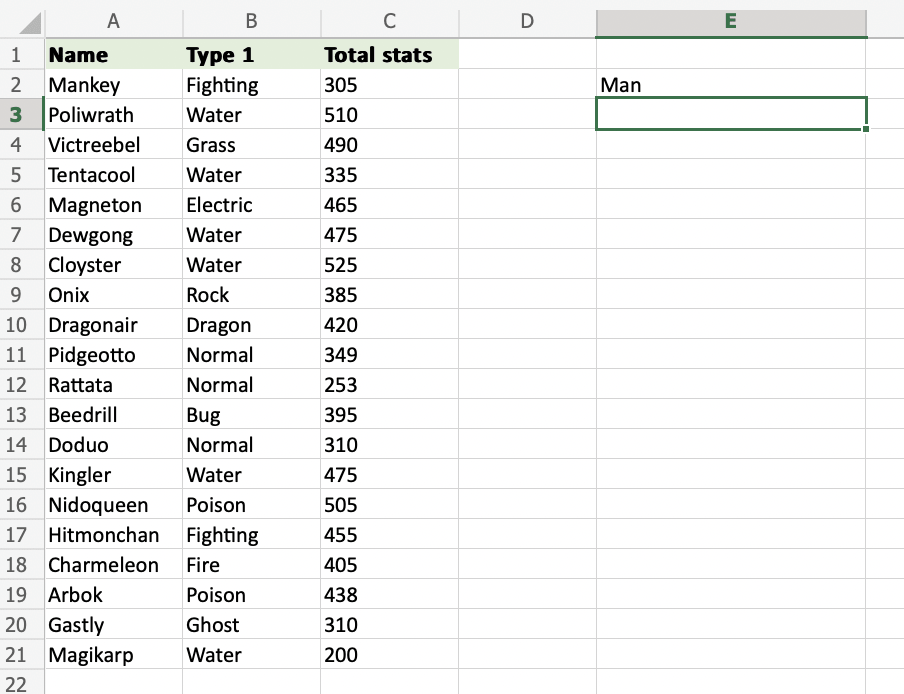
=LEFT(A2) uses the default funcion of LEFT and retrieves the first symbol from the A2 cell.
How to Use the LEFT Function with a Defined Length of Characters
Learn to use =LEFT to get more than one character.
Step 1) Start the LEFT function
- Select a cell
E2 - Type
=LEFT - Double click the LEFT command
Note: The different parts of the function are separated by a symbol, like comma , or semicolon ;
The symbol depends on your Language Settings.
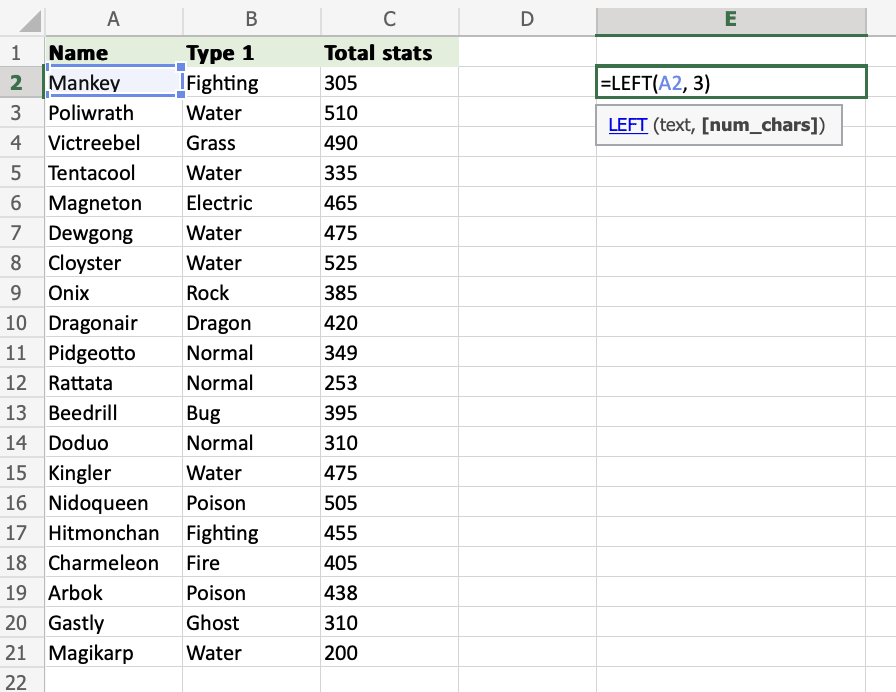
Step 2) Select cells and set the number of characters
- Enter the cell name (
A2) and define the length of characters you want to retrieve, using a,as a delimiter (A2,3) - Hit enter
The function returns the first 3 characters from cell A2.
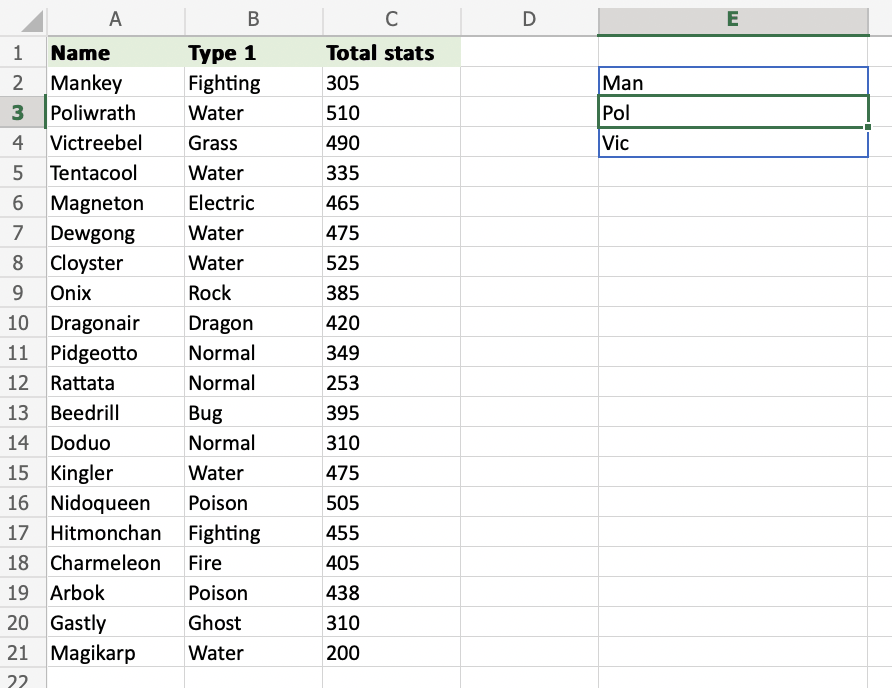
How to use the LEFT Function on a Range of Cells
Step 1) Start the LEFT function
- Select a cell
E2 - Type
=LEFT - Double click the LEFT command
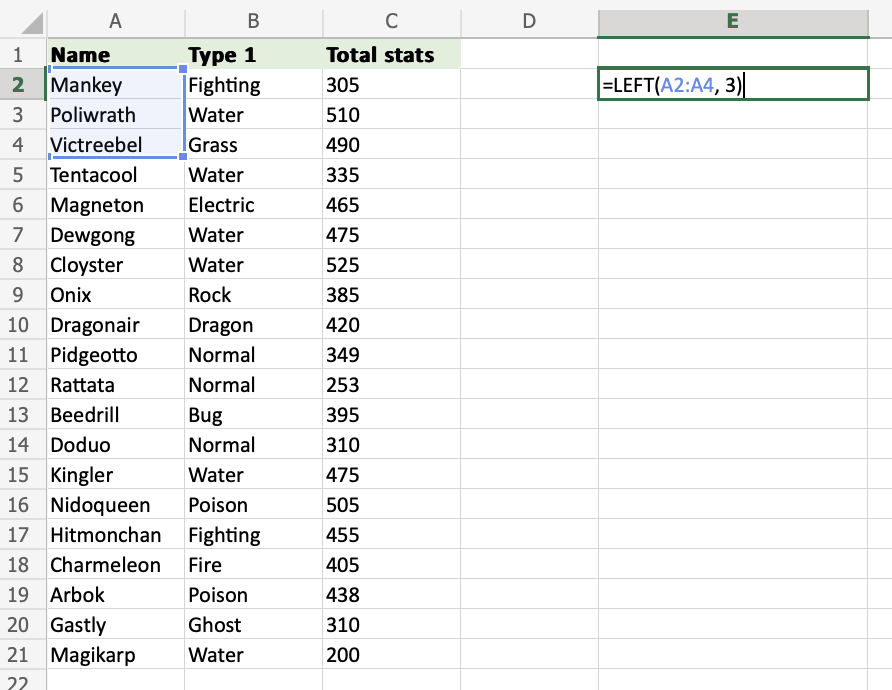
Step 2) Select cells and number of characters
- Select the cells (
A2:A4) and define the length of characters you want to retrieve, using a,as a delimiter (A2:A4,3) - Hit enter
The function returns the first 3 characters from each cell within the range A2:A4.